Paraphrasing effectively while avoiding plagiarism is a common pain point for writers across all levels of expertise. The fear of accidentally plagiarising someone else’s work or failing to give credit where it’s due can plague you from even starting to write.
However, instead of fearing, prepare yourself with this step-by-step guide to learn how to paraphrase without plagiarism. Whether you’re a student racing against a deadline or a researcher aiming for accuracy and originality, this guide is the key to effectively paraphrase for plagiarism-free academic writing.
What is Paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is the act of restating someone else’s ideas or information in your own words. It involves expressing the same meaning as the original text but using different words and sentence structures.
Paraphrasing is commonly used to avoid plagiarism, integrate evidence into writing, and simplify complex information for better understanding. It’s an essential skill in academic and professional writing, allowing writers to convey information effectively while maintaining originality and clarity.
Understanding Paraphrasing, Quoting, and Summarizing
When writing an academic paper, you will likely need to incorporate source material to support your ideas and analysis. There are three main ways to do this – paraphrasing, quoting, and summarizing. However, each approach varies in how closely your writing reflects the original source.
- Paraphrasing
- Rephrases the original text in your own words
- Should condense the original information using different phrasing and sentence structures
- Retains the full meaning of the original text
- Must always attribute the source using in-text citations
- Quoting
- Uses the exact words from the original source
- Places word-for-word passages in quotation marks
- Should quote briefly to highlight key phrases or ideas
- Must match the original exactly
- Requires in-text citations to attribute quotes
- Summarizing
- Puts the main points of a passage into your own words
- Greatly condenses the original to provide a broad overview
- Much shorter than the original text
- Must include attribution to the original source
Using the appropriate mix of quotes, paraphrases, and summaries adds credibility to your content by referencing source texts. This demonstrates your authority on the topic and ensures academic honesty through proper citation. Here is a draft section on when to paraphrase:
When to Paraphrase?
Paraphrasing is an essential skill in academic writing and could be used for following purposes:
- To Clarify Ideas
Paraphrase when you need to clarify or simplify a short, complex passage from a source text to ensure better reader comprehension. This demonstrates deep understanding of difficult concepts on the author’s part.
- To avoiding Over-Quotation
Choosing to paraphrase instead of relying heavily on direct quotations enables the smooth integration of external ideas in your own writing style.
- To Eliminate Non-Essential Wording
When the original text contains non-essential wording, paraphrasing allows you to focus selectively on the most relevant information and explain the main points, enhancing clarity and conciseness.
- To Reporting Statistical Data
Paraphrase when you need to report numerical data or statistics. This is preferred in APA format over directly quoting such information.
Strategies on How to Paraphrase Without Plagiarising
It is important to thoroughly understand the original text to grasp its main ideas before paraphrasing. Then to effectively paraphrase in order to avoid plagiarism and yet convey the information you can adopt a combination of following strategies:
- Use alternative vocabulary
This strategy involves replacing key terms in the original passage with synonyms, adding variety and clarity to the text.
Example:
Original text: The scientist conducted experiments to test the credibility of the study
Paraphrased text: The researcher carried out trials to evaluate the reliability of the study
- Modify the parts of speech
Modifying the grammatical structure of sentences can provide a fresh perspective. For instance, modifying the parts of speech by changing an adjective to an adverb can rephrase a sentence. However, its effectiveness relies on the wording of the original passage, thus it must be used in combination with other strategies.
Example:
Original text: He is a careful driver.
Paraphrased text: He drives carefully.
- Changing the structure
Reorganizing the sequence of phrases and clauses can lead to new sentences while preserving the original meaning. When doing so, use active voice whenever possible and reserve passive voice only for situations when it is absolutely necessary.
Example:
Original text: The chef carefully prepared the ingredients before cooking the meal.
Paraphrased text: Before cooking the meal, the chef meticulously prepared the ingredients.
- Adding or removing piece of content
Adjusting the content by adding or omitting information can help tailor the paraphrased version. You can add your own take on an existing quote to elaborate on the context. While doing so, it must be ensured that the core message remains unaltered.
Example:
Original text: Reading for pleasure fosters creativity and empathy in children.
Paraphrased text: Engaging in recreational activities such as reading can stimulate creativity among youngsters.
- Citing your sources
If you use a specific phrase from the original, enclose it in quotation marks and attribute it correctly. Always cite the original source, including author, title, publication date, and other relevant details. Proper paraphrasing and citation prevent plagiarism and enhance your work with valuable sources.
Example:
Original text: The amendment made changes to Section 40 of the Voting Rights Act, which bans any voting practice that discriminates against racial or language minorities.
Paraphrased text: The amendment in 2020 updated Section 40 of the Voting Rights Act, making it illegal to have any voting practices that are discriminatory towards racial or linguistic minority groups (Smith, 2020).
Further, use paraphrasing tools for streamlining the process of efficient and employ plagiarism checker tools to establish the authenticity of your content.
Using AI Effectively to Paraphrase Without Plagiarism
One of the most efficient ways to rework existing content is by using an advanced paraphrasing tool.
Trinka’s paraphrasing tool offers a customised and error-free paraphrasing option. Its user-friendly interface makes on-demand paraphrasing highly accessible. Within seconds, Trinka delivers reworked content that maintains meaning while transforming vocabulary and style.
Features:
- Multiple paraphrasing options to choose from
- Customizable degree of variation
- Automatic grammar error correction
- One-click, instant paraphrasing
Benefits:
- Clarity and Precision – Help academic writers maintain clarity, accuracy, and proper usage of technical terminology by transforming text while preserving its original meaning, ensuring that the content remains clear, precise, and academically
- Maintaining Academic Integrity – Assist writers in avoiding plagiarism by rephrasing content in their own words while still accurately conveying the intended message, thus upholding academic integrity
- Efficiency in Research Writing – Enhances the efficiency by quickly rewording text, saving time for researchers to focus on analyzing data, conducting experiments, and developing original insights, without being hindered by manual rephrasing tasks
4 simple steps to follow to paraphrase using Trinka
Step 1: Input the desired text into the left panel after selecting the ‘Paraphraser’ option from the vertical toolbar on the right.
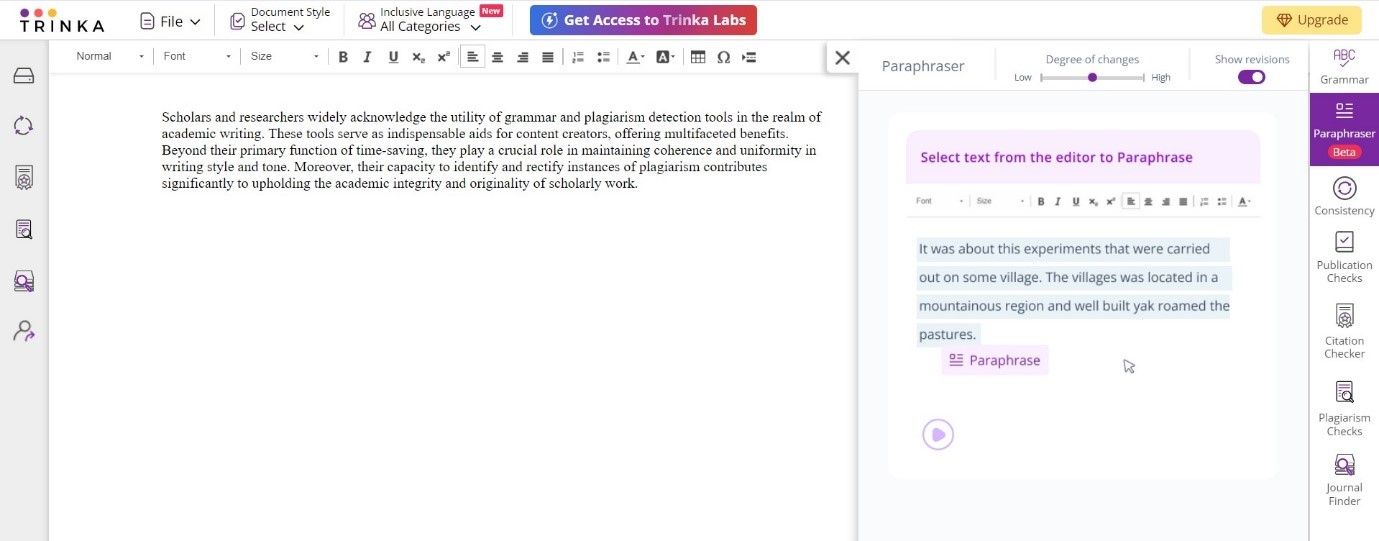
Step 2: Choose either specific sentences or the entire content for paraphrasing.
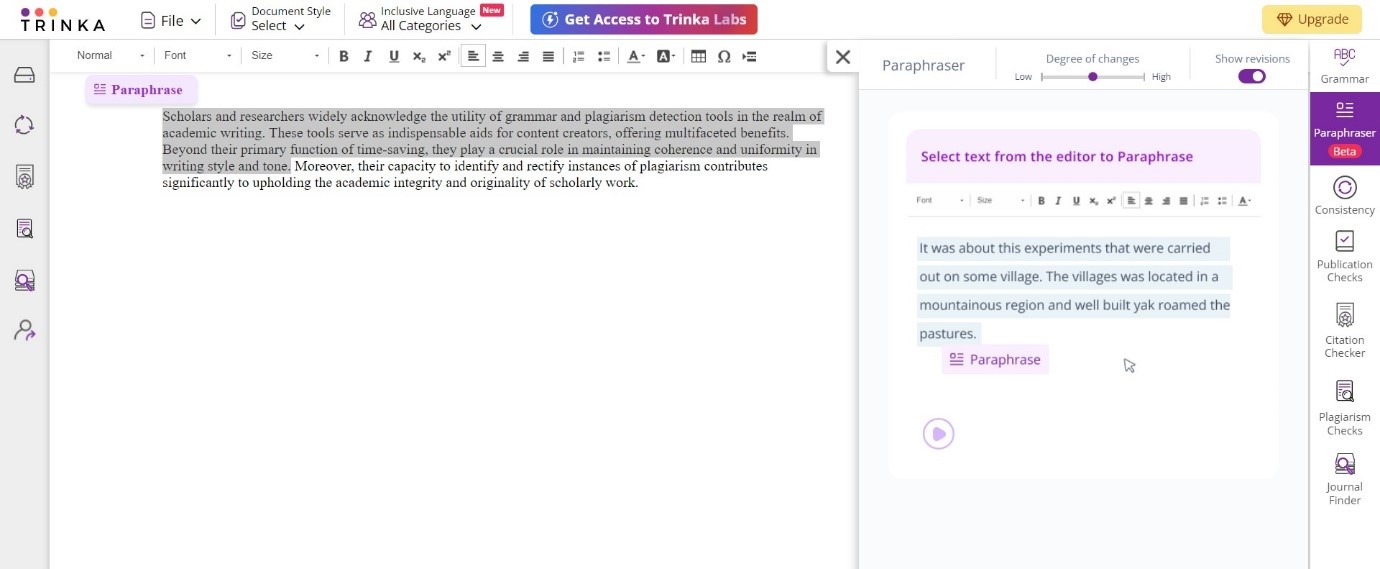
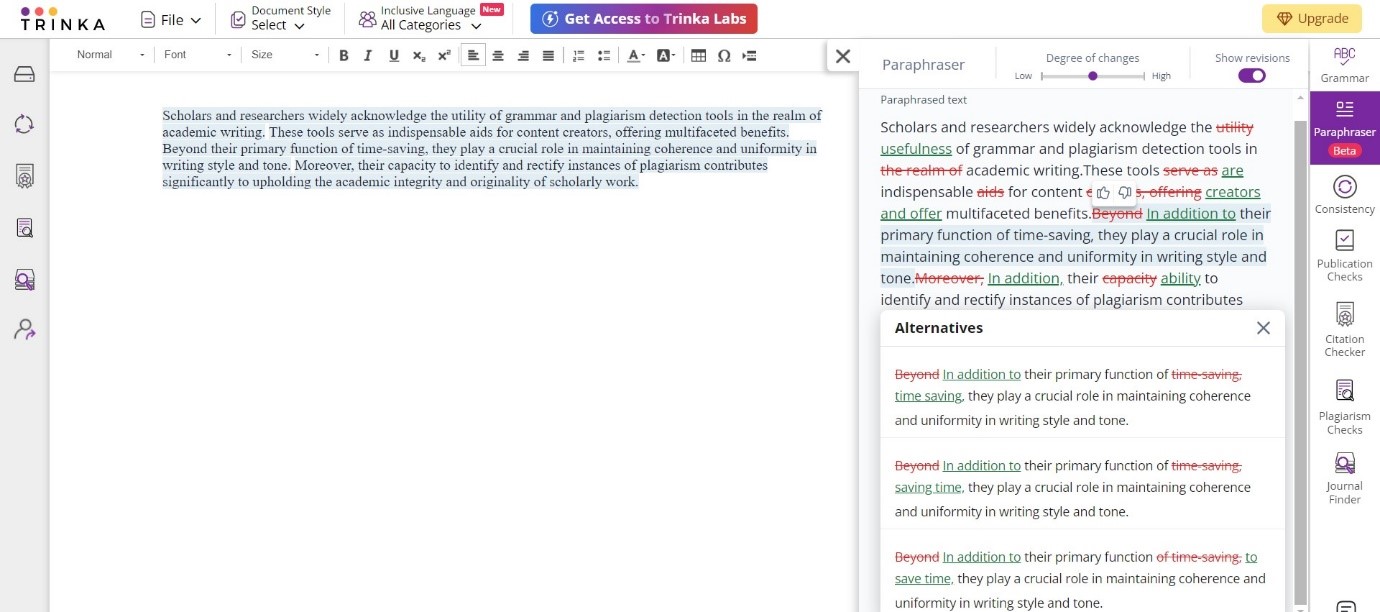
Step 3: Adjust the degree of change desired using the options at the top of the right panel. The paraphrased text will be displayed in the right panel. Further alternatives can be explored by clicking on suggested paraphrases.
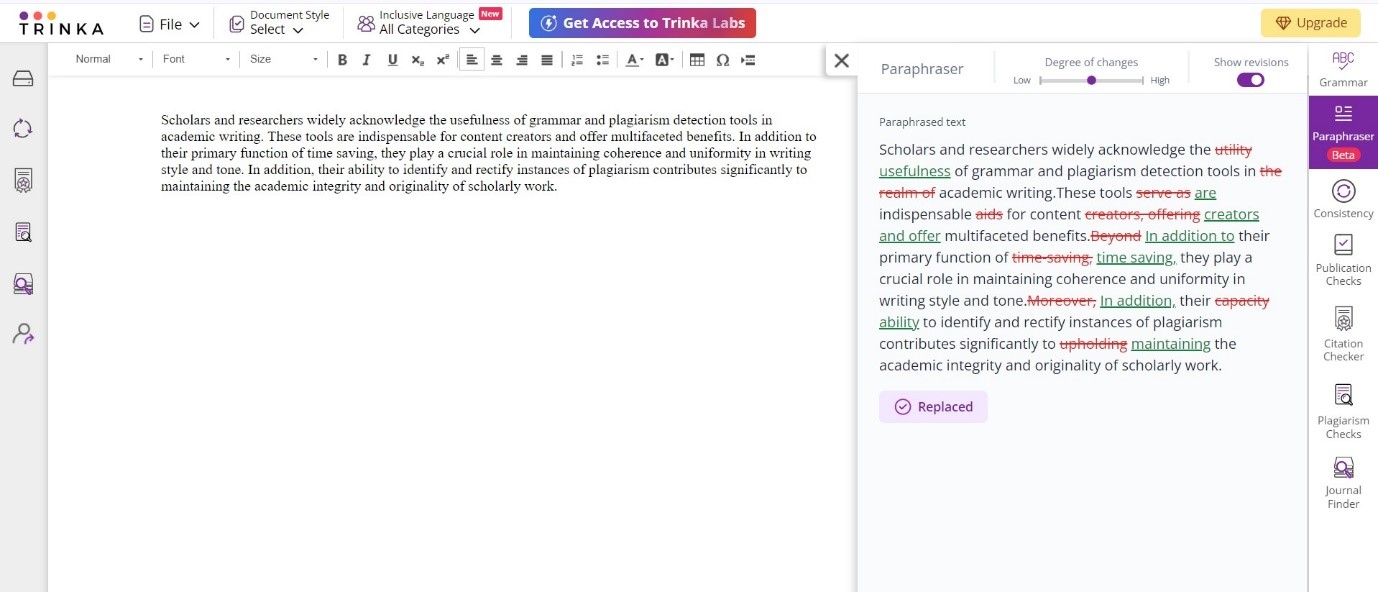
Step 4: Once satisfied with the alternatives, the paraphrased content is finally ready for your use.
Paraphrasing is a valuable skill for effectively integrating sources into your writing while avoiding plagiarism.
By following a step by step approach outlined above and understanding the examples, you can master the art of paraphrasing and enhance the clarity and originality of your work.
FAQ's on Paraphrasing
Effective paraphrasing involves understanding the original text, expressing its ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, and properly citing the source.
To paraphrase a quote, read the original text carefully, understand its meaning, and then rephrase it in your own words without changing the original intent. Ensure that the paraphrased version accurately reflects the original idea.
When paraphrasing, you must still give credit to the original source. Use an in-text citation that includes the author's name and the publication year, followed by a reference entry in the bibliography or works cited page.
To paraphrase a sentence, read it thoroughly, understand its meaning, and then rewrite it using different words and sentence structure while retaining the original idea. Be careful not to change the meaning or misrepresent the original text.
In APA format, paraphrasing requires providing the author's name and the publication year in the in-text citation. Additionally, include a full reference entry in the references list at the end of your document.
To paraphrase without plagiarizing, ensure that you fully understand the original text before rewriting it in your own words. Use proper citation to acknowledge the source, and avoid closely mimicking the original text's structure or wording.
When paraphrasing a research paper, focus on conveying the author's ideas accurately while using your own words and sentence structure. Ensure that the paraphrased content is coherent and properly cited according to the required citation style, such as APA or MLA.

